Total and Marginal Utility
The utility refers to the degree of satisfaction that receives the consumer to purchase a particular product. To some extent, while consumers purchase more units per unit time, the higher the total utility received. Although, the total utility increases, the marginal utility receiving consuming each additional unit of the good usually decreases.
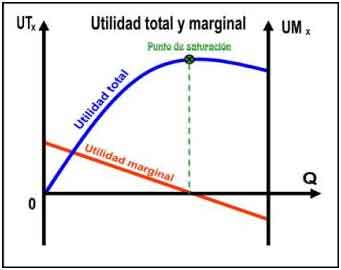
Total and Marginal Utility Graph
The saturation point corresponds to a level of consumption in which the total utility is maximum. Where the marginal utility is zero. The additional units of the product cause the total utility to decrease and the marginal utility becomes negative due to storage or sales problems. Graphically, they can be represented as follows:
Consumer Balance
Based on the assumption of consumer rationality, its objective will be to maximize its total utility. Nore the satisfaction derived from the expenditure of its income. In doing so it is said that the consumer is in equilibrium, which corresponds to the case in which the income is spent. In such a way that the utility or satisfaction of the last money spent on the different articles is the same. By numbering goods as 1, 2, …, N, this can be expressed mathematically as:
With the following restriction:
Where I is the income of the consumer.
Indifference Curves
An indifference curve shows the various combinations of Article X and Article Y that produce the same degree of utility or satisfaction to the consumer. So the consumer tastes and balance can also be demonstrated by indifference curves. Thus a curve of indifference superior to others, which represents a greater degree of satisfaction. The indifference curves have negative slopes, are convex to the origin and cannot be crossed.
All points on the same indifference curve provide identical consumer satisfaction. Hence the points on the indifference curve II indicate greater satisfaction than the points on the curve I. However less than the points on the curve III . In this way, only the order or range of preferences of a consumer is required to be able to trace their indifference curves.
Marginal Substitution Rate
The marginal rate of substitution of X by Y ( TMS XY ) refers to the amount of Y. That a consumer is willing to give for an additional unit of X and stays on the same indifference curve. As the individual moves downward in an indifference curve, the XY TMS decreases.
Explanation
The consideration of families as owners of the productive and income-earning resources is analyzed elsewhere in this course. Here we will consider them only as demanders of goods and services. So we will refer to these economic agents with the term ‘consumers’.
By analyzing consumption at the end of the last century, neoclassical economists, following the ideas of utilitarian philosophy of Jeremy Bentham. They assumed that the mainspring of individuals by demanding goods and services was to obtain the highest possible profit. So they observed that the usefulness of the consumption of a good depends, among other things. Basically on the amount of that good that has consumed the individual. Thus they established the distinction between total utility. In fact the utility that provides all the consumed amount of good, and the marginal utility. Therefore the increase in total utility that produces the last unit consumed of that good. They noted also that the increasing consumption of goods produced satisfaction for each new unit is less than that produced by the above. So concluded that the marginal utility is decreasing.
Example
Suppose that we went into a pastry for a snack. The first sweet will give us much satisfaction. Then the second we will not like it so much. If we continue taking cakes, there will come a time when we will feel satiated. Any cake consumed after satiety will be unpleasant. So the marginal utility of cakes, that is, the utility provided by the last cake consumed, has been getting smaller and smaller until it becomes negative. The image graphically represents the total utility, at the top. Also the marginal utility produced by the cakes in our example.
Note that the height of the “steps” of total utility coincides with the size of the marginal utility steps. In fact, the total utility perceived by the consumption of four cakes. Actually is equal to the total utility perceived by the consumption of three cakes. Moreover the utility produced by the fourth, that is, by its marginal utility.
This representation of the utility has been presented in discrete form , i.e., considering the effect of each cake one by one. We could have considered the utility produced by each half cake, or for every quarter of cake. Nor for small pieces of cake that we want. In doing so, the width of each step would be reduced to a single point and the ladder would become a curved line. Hence this is a presentation of the utility continuously.
More from Business Study Notes:- Roles and Functions of Capital Market
If an individual is offered the possibility of acquiring units of two types of goods. Then he will choose the one that gives him greater satisfaction, that is, one whose marginal utility is greater. If you are offered the option to choose again you will use the same criteria over and over again. As a consequence, the marginal utility of the most palatable good will diminish to match that of the other. Therefore if we consider the argument of many goods it remains the same. So that the marginal utility of all goods consumed tends to equalize.
Money is useful: it allows us to acquire other goods and services and provides us with much peace and security for the future. The marginal utility of money, like that of any other good, is decreasing. If we have acquired many goods and have little money left. Then its marginal utility will be high so we will keep it without exchanging it for other goods. If our income increases, that is to say, if the amount of money available increases. Then the marginal utility of each peseta will be lower than that of other goods. So that we will increase our demand for them.
The shape of the demand curve, its decreasing slope, and its convexity towards origin, is precisely the consequence of the analysis of marginal utility. Although by increasing the quantity demanded, its marginal utility is decreasing. So we will be willing to pay each time less money for the product.

Hello everyone! This is Richard Daniels, a full-time passionate researcher & blogger. He holds a Ph.D. degree in Economics. He loves to write about economics, e-commerce, and business-related topics for students to assist them in their studies. That's the sole purpose of Business Study Notes.
Love my efforts? Don't forget to share this blog.