When it comes to the introduction to project management, here it is important to understand the project management first. Project management is the field of organizing & managing resources in an effective manner, so that these resources provide all the needed work to complete a project within specified scope, cost & time limitations. In fact the project is one-time and temporary effort to develop unique product or service that results in the addition of value or beneficial change. This one time & temporary undertaking make the project different from operations or processes which are semi-permanent or permanent continuous functional work to develop same product or service repeatedly. All these facts are included in the introduction to project management.
Introduction to Project management
The first challenge of the project management is guaranteeing that a project is completed within the specified constraints. The optimized allocation and integration of the inputs required to accomplish those pre-specified objectives is the second challenge. Thus the project is effectively chosen group of activities selected to utilize resources in order to fulfill the objectives set by the organization.
Management in any project is associated with productivity which includes efficiency & effectiveness. These components of productivity are as follow.
Efficiency
The reduction in the resource costs by the management is said to efficiency of the management. In simple words “doing things right” is the efficiency.
Effectiveness
The completion of the activities by the management is referred to as effectiveness of the management. In simple words “doing right things” is the effectiveness.
The efficiency is associated with means and effectiveness is linked with the ends. These are interconnected. It is possible to become effective even when efficiency is ignored. For some there are certain companies that are potentially effective but are very inefficient. Their tasks are completed but at increased cost. So for management of particular project, it is necessary to complete all the activities but also in an efficient manner. Following diagram reflects the management trying efficiency and effectiveness
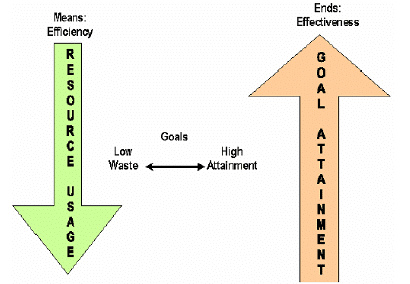
Efficiency and Effectiveness
The Project Management System
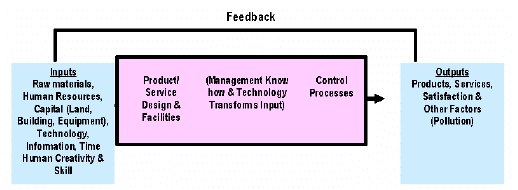
Project Management System
Some people argue that survival is important driving force because of the interrelatedness of these driving forces. The implementation of project management becomes easier when the company identifies that its survival is at stake. The comprehension of driving forces by the organization provides the basis for the speed by which companies attain some degree of maturity in project management.
The Project Manager
The professional in the field of project management is said to be project manager. Project manager is responsible for planning & execution of particular project. The success of the project is ensured by the project manager by reducing the risk throughout the lifetime of the project. There are many formal & informal methods for this purpose. The project manager should generally ask the acute questions, point out the unclear assumptions and settle interpersonal disputes. These tasks should do with systematic management skills from throughout the end of the project.
Types of Project Manager
There are certain elements of external environment that should be understood by the project managers in order to perform their tasks effectively. These external factors include political, economic, social, technological and ethical forces that influence the operations of the project. Following are the main types of project managers.
- Line Managers
- Staff Managers
- Functional Manager
- General Manager
- Administrator
Line Manager
Line managers are the ones who have the responsibility for activities that contribute directly in the manufacturing of basic product or services of the organization.
Staff Managers
Staff managers are responsible for supporting the working of the line managers through their special technical expertise.
Functional Managers
Functional managers are concerned with only single activity area, i.e. marketing, finance, personnel, production, sales or accounting
General Mangers
Complex organizational unit is managed by the general managers that contain many areas of functional activity.
Administrator
The person who administers the work in certain organization is called administrator.
Activities of Project Managers
Project managers undertake the following four kinds of activities
- Traditional Management
This contains planning, controlling & decision making activities
- Communication
Exchanging of routine information and processing paperwork are included in this category
- Human Resource Management (HRM)
The disciplining, motivating, staffing, managing conflict and training activities are included in this category
- Networking
Interacting with outsiders and socializing activities are included in this head Average manager utilizes
- 32% of total time in formal management activities
- 29% time in communicating activities
- 20% time in HRM activities
- 19% time in networking
Success for Project Managers
For accomplishing permanent success as project manager, there are three general preconditions which are as follow
- Ability (A)
- Motivation to Manage (M)
- Opportunity (O)
The basic formula of managerial success (S) is composed by these three elements.
S = A x M x O
10 Facts of Project Managerial Life
Following are the significant ten facts of project managerial life.
- Project managers work many hours. As one progress to next managerial level, his working hours increases.
- Project managers are busy and their whole day is divided into hundreds of brief episodes or incidents. As the rank in the management ladder increase, the rate of activity decrease.
- The work of the project managers is fragmented. The managers having high activity level can devote little time to one activity. Discontinuity and interruptions are common.
- Project managers have varying jobs. They are involved in different kinds of activities like phone calls, paperwork, scheduled and unscheduled meetings etc. They deal with different content areas and interact with variety of people.
- Most of the time of projects managers passes within the organization by performing different activities. That is why they are also considered as homebodies. When the rank of the manager increases, he spends more time in activities that are outside his work area & organization.
- Generally the project managers perform oral work. At each managerial level, most of their time is spent in communicating verbally by telephone or personal contact.
- A lot of contacts are used by the project managers. Project managers exchange information with subordinates, superiors, peers and outsiders on continuous basis in accordance with their high level of verbal communication.
- Project managers do not perform reflective planning. Reflective planning requires sufficient time which is not available to project managers due to interruptions.
- The basic ingredient of work of project managers is information. Managers utilizes much of their time in getting, interpreting and providing information.
- Project managers have not awareness about their spending time. Managers constantly overestimate the time they utilize in reading & writing, production, thinking, calculating and phone calls. Similarly they constantly underestimate their time utilizing on informal discussions as well as meetings.
Managerial Skills
The ability or proficiency in conducting certain task is said to be a skill. The ability to translate actions into results is reflected in skills. Managerial skills are of the following types.
- Technical Skills
Technical skill refers to the knowledge and proficiency in activities containing processes, procedures and methods.
- Human Skills
The ability to work with people is covered in human skill. It refers to the team work and cooperative effort in which everyone has security & freedom to express his opinion.
- Conceptual Skill
It refers to the capacity to view big picture so that important elements of the situation are identified and the relationships among these elements are understood.
- Design Skills
Design skill refers to the ability to solve problems in a manner that will benefit the organization.
Project Driven Vs Non Project Driven Organizations
All organizations at micro level are manufacturing, engineering or marketing driven. But organizations are project driven or non-project driven at macro level. All work is performed through projects in project driven organizations like construction or aerospace. Each project in the project driven organization has its own profit & loss statement and separate cost centre. The summation of the profits on all projects is simply the total profit of the organization. Furthermore everything centers on the projects in project driven organizations. On the other hand in non-project driven organizations profit & loss is evaluated on vertical or functional lines like low technology manufacturing organization. In such non-project driven organizations, projects exist seldom to support functional lines or product lines. Revenue-producing functional line activities are assigned resources on priority basis as compared to the projects.
Project management is more difficult in non-project organizations due to the following reasons.
- Projects can be limited and far between.
- The project management requirement is not same for all projects and therefore they cannot be identically managed. This difficulty consequence from poor comprehension of project management and hesitation of companies to invest suitable training.
- Because approvals often follow the vertical chain of command, therefore the projects tend to delay. Resultantly there is too long project work in functional departments.
- Only limited portion of the organization comprehends project management and views the system in action because project staffing is on local basis.
- The dependency on subcontractors and outside agencies is high for the purpose of project management expertise.
There are certain Hybrid organizations which are generally non-project driven but have one or two divisions which are project driven.

Hello everyone! This is Richard Daniels, a full-time passionate researcher & blogger. He holds a Ph.D. degree in Economics. He loves to write about economics, e-commerce, and business-related topics for students to assist them in their studies. That's the sole purpose of Business Study Notes.
Love my efforts? Don't forget to share this blog.




